Understanding Proximal Hamstring Tendinopathy
Proximal Hamstring Tendinopathy: The Basics
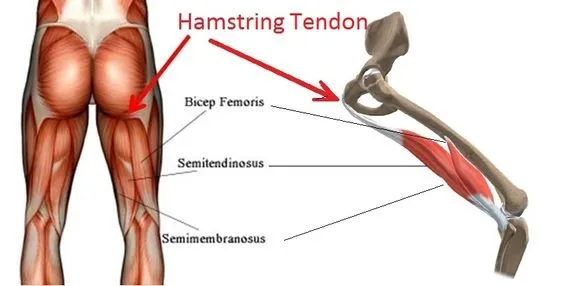
1. Anatomy
To understand proximal hamstring tendinopathy, let’s start with the anatomy. The hamstring muscles transition into tendons, attaching to the ischial tuberosity, also known as the sitting bone. The location of tendon pathology can vary, and studies show considerable variability among individuals.
2. Causes of Proximal Hamstring Tendinopathy
PHT is often triggered by factors like compression and tensile load. Tensile factors, such as increased speed in activities like running, can elevate the demand on the tendon. Compression factors, like hip flexion during activities such as running uphill or cycling, also contribute to the condition.
3. Symptoms
Symptoms typically manifest as deep, localized pain around the sitting bones and worsen after activities like running, squatting, or sitting. The characteristic warm-up effect, where symptoms lessen as the tendon warms up during activity, is common in the early stages.
Tests and Differential Diagnoses
1. Show Off Test
One at-home test involves standing, wearing shoes, and bringing the heel to the front of the other foot, simulating a scraping motion. If this triggers pain in the high buttock area, proximal hamstring tendinopathy may be implicated.
2. Wall Heel Press Test
Stand close to a wall, back against it, and lift the symptomatic leg, attempting to press the heel into the wall. Pain during this test could indicate proximal hamstring tendinopathy.
3. Differential Diagnoses
If symptoms become diffuse or spread to other areas, it might suggest involvement of the lumbar spine, hip, sacroiliac joint, or nerve-related issues. Seeking professional assessment is crucial for an accurate diagnosis.
Risk Factors
Excessive static stretching, as in certain yoga or Pilates postures, is suggested as a potential risk factor. Awareness of these risk factors can aid in preventing flare-ups and managing the condition effectively.
Conclusion
Understanding hamstring tendinopathies involves grasping the anatomy, recognizing causative factors, and being aware of symptoms and risk factors. Stay tuned for the next episode, where we’ll explore tendon rehab and prevention strategies. Remember, knowledge is power in taking control of your rehabilitation journey.

